
Unusual sources include exposure to methylene chloride, which is metabolized to CO and hemolysis, with increased metabolism of hemoglobin.

CO poisoning occurs from breathing in elevated air levels of carbon monoxide. The most common location of exposures causing CO poisoning are in homes and less commonly in workplaces. Sources of CO include: boilers: furnaces, cars and trucks, generators and other gasoline or diesel-powered engines, gas and propane heaters, woodstoves, gas stoves, fireplaces, tobacco smoke, forklifts, and fires. CSTE Position Statement(s)Ĭarbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, nonirritating gas that is produced through the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing substances.
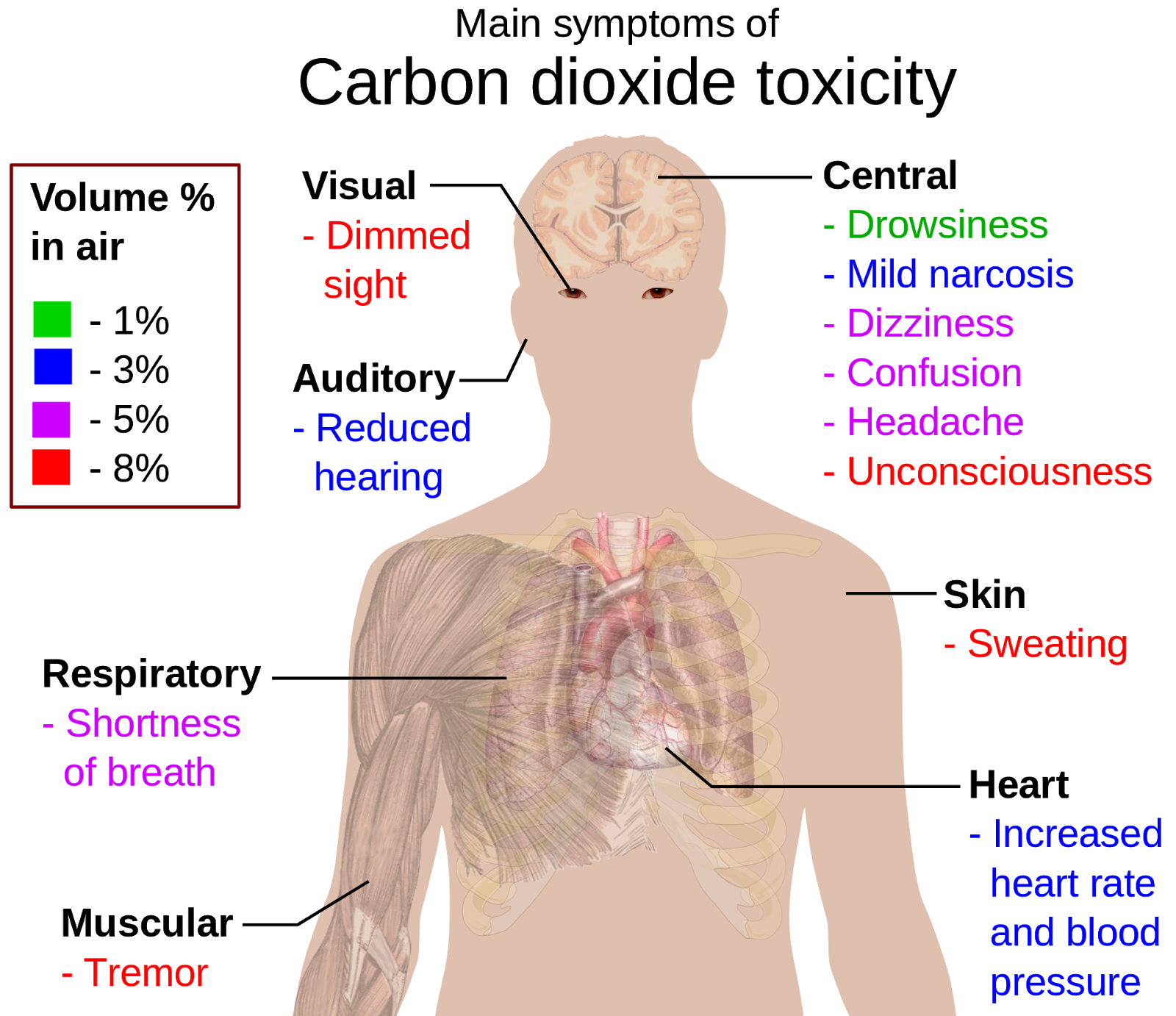
CARBON DIOXIDE DEFINITION HOW TO
Surveillance case definitions are not intended to be used by healthcare providers for making a clinical diagnosis or determining how to meet an individual patient’s health needs. Surveillance case definitions enable public health officials to classify and count cases consistently across reporting jurisdictions. Print NOTE: A surveillance case definition is a set of uniform criteria used to define a disease for public health surveillance. Event Codes & Other Surveillance Resources.Implementing Arboviral Case Notifications.Implementing an HL7 Message Mapping Guide.HL7 Implementation & Onboarding, Technical Assistance plus icon.Supporting Documents for Implementation.HL7 Message Mapping Guides & Standards plus icon.About Notifiable Noninfectious Diseases and Conditions Data.Notifiable Noninfectious Disease Tables plus icon.About Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions Data.Notifiable Infectious Disease Tables plus icon.Case Surveillance Modernization plus icon.National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS) Home.Integrated Surveillance Information Systems/NEDSS.How We Conduct Case Surveillance plus icon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
